The processing sample of Pu’er tea was studied by headspace-solid phase microextraction (HSPME) (HS-SPME) enriched in its aroma compounds and GC-MS the changes of aroma components in Pu’er tea during processing were studied by analysis of aroma components. The results showed that the contents of alcohols and hydrocarbons in aroma components decreased sharply, while the contents of heterooxides and esters increased significantly. 1,2,3-trimethoxybenzene is the most abundant component in the hetero-oxide compounds, and reaches the highest content after the end of the heap. In addition, several chemical components with obvious difference in relative content of aroma components of Shaying Qingmao tea and Pu’er tea were further analyzed. Keywords: Pu’er tea; aroma; HS-SPME; change; process; heap

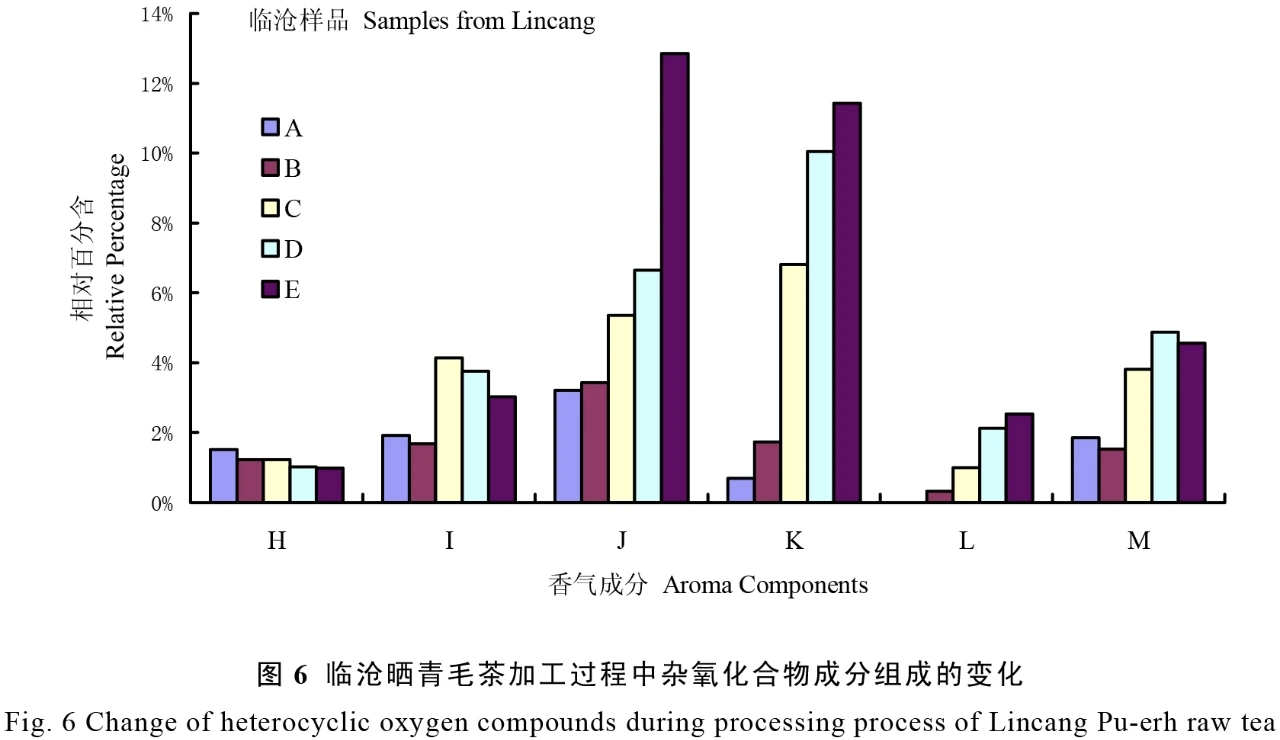
Abstract: Taking the processing samples of Pu ‘er tea as the research object, the headspace – solid phase microextraction method (HS-SPME) was used to enrich its aroma substances and GC-MS was adopted for the analysis of aroma components, and the changes in the composition of aroma components during the processing of Pu ‘er tea were studied. The results show that during the piling process of sun-dried green tea, the alcohol and hydrocarbon components in the aroma components decrease sharply, while the heterooxide and ester components increase significantly. 1,2, 3-trimethoxylbenzene is the most abundant component among heterooxides and its content reaches the highest after the piling is completed. In addition, several chemical components with relatively obvious differences in content in the aroma components of sun-dried green tea and Pu ‘er tea were further analyzed. Key words: Pu ‘er tea Aroma HS-SPME Change Processing Piling Pu ‘er tea is produced from the sun-dried green tea of the large-leaf tea [Camellia sinensis (Linn.) var.assamica (Masters) Kitamura], which is unique to Yunnan Province, through a special post-fermentation process. Due to its unique aroma (aged fragrance) and health benefits [1], Pu ‘er tea has attracted much attention from consumers both at home and abroad in recent years. The unique aroma of Pu ‘er tea is formed during the fermentation process after piling. The piling process is a crucial procedure in shaping the quality of Pu ‘er tea. Essentially, it uses the internal components of sun-dried green tea as the base and undergoes a series of biochemical reactions under the influence of moisture, heat and microorganisms, thus forming the unique quality style of Pu ‘er tea. According to relevant research reports, an important characteristic of the aroma components of Pu ‘er tea lies in the formation of a large number of aromatic compounds during the piling process, such as 1,2, 3-trimethoxylbenzene, 1, 2-dimethoxylbenzene, etc. Many substances with typical musty and aged aromas in fermented tea may be formed through methylation reactions of corresponding compounds under the action of mold [3]. In addition, different drying methods [4] and different storage times [5] all have a significant impact on the aroma of Pu ‘er tea. The aging process can increase the volatile substances in Pu ‘er tea [6]

Test material: there were 15 samples in total from 3 batches during the processing process of sunburned green tea. From Wenshan, Dali and Lincang, samples are taken sequentially during the processing of the waste stack, the details are as follows: raw material of sun-cured green tea (A), first dump sampling (B), second dump sampling (C), third dump sampling (D), the finished products (E) shall be discharged from the stack, and the samples shall be dried at 120℃ solid sample. Main test instruments: HH- 2 digital display constant temperature water bath (Jiangnan Instrument Factory); self-made improved extraction bottle, manual SPME sampler and 65μm PDMS/DVB solid phase microextraction head (US Supelco manufactured by the company), Agilent GC6890N-5973 mass selective detector(MSD).





Health tea
black tea pu er tea
YM’s own tea mountain Choose high-quality organic tea